User Libraries in Eclipse (RAD)
I imagine most folks who use Eclipse or its variants already know about this, but just in case…
User Libraries are reusable groupings of jar files that compose a particular library to be used by an application. This is a much easier way to manage the jars needed by your projects than simply adding them one-at-a-time to the Build Path and/or the WEB-INF/lib directory for execution on a local server.
Creating and Managing User Libraries
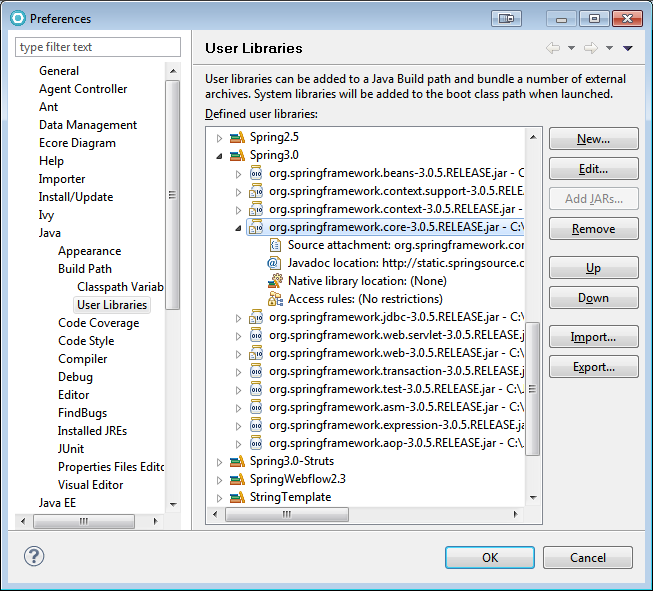
Window > Preferences > Java > Build Path > User Libraries
Add as many User Libraries as your applications require. Name them so that you can distinguish versions from each other when you work with applications that use different versions of the same library.
Use the “New” button and type a meaningful name, then the “Add JARs” button to locate specific jar files to include.
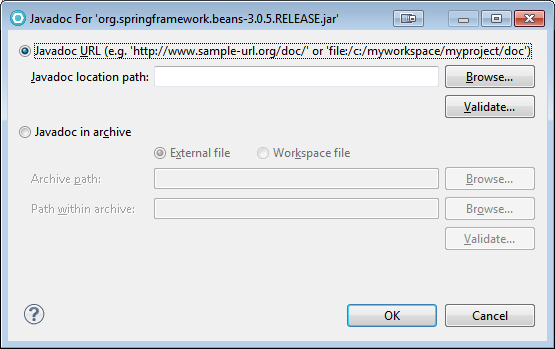
You can attach a javadoc URL to a library, which will give you more useful help within Eclipse when you’re using that library. Expand the added jar file (the small triangle), select the Javadoc location line, and click the “Edit” button. You can point at either local javadoc files or a remote URL.
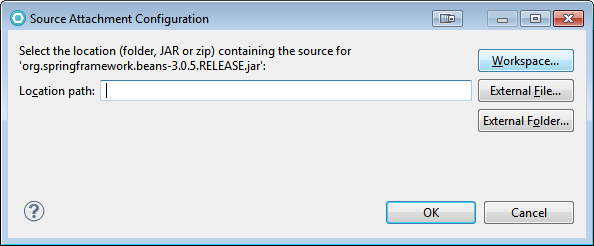
Similarly, you can attach a source code file or folder to a library, which will enable you to trace into its source if necessary.
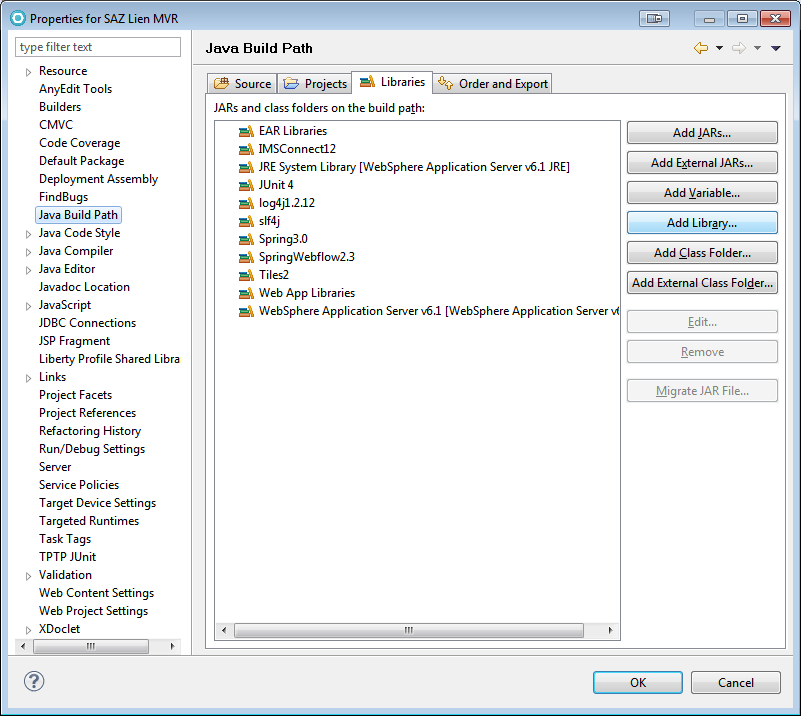
Adding User Libraries to the Build Path
Project > Properties > Java Build Path
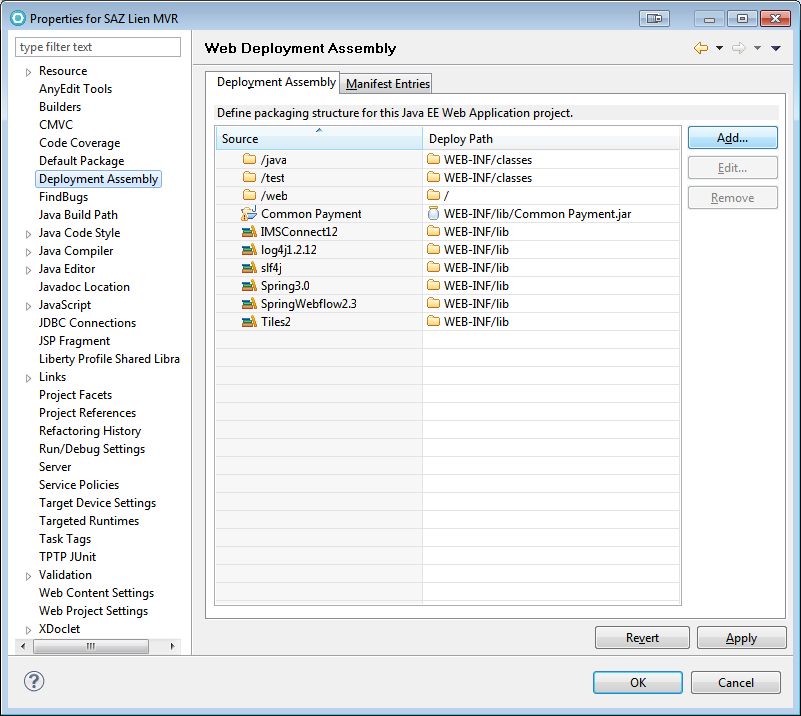
Adding User Libraries to the Execution Path (JEE Deployment)
Project > Properties > Deployment Assembly